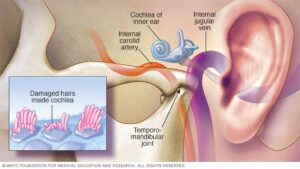
Tinnitus is a common problem experienced by nearly 15-20% of people from all age groups. It is characterized by a soft or loud/high-or low-pitched sound (ringing) in either one or both the ears or even in the head while there is no external source of the sound. Tinnitus could be accompanied by hearing loss.
Other than ringing in the ears, a person with tinnitus could also experience buzzing, roaring, clicking, hissing, or humming sounds.
Causes of Tinnitus:
Tinnitus is not a disease but, it is a symptom caused by some of the problems (cumulative noise exposure, ear infections, and certain heal and neck injuries) affecting the auditory system including the ear, auditory nerve and other parts of the brain, involved in the processing of the sound. You will be amazed to know that blockage of the ear canal by a piece of earwax may result in tinnitus. However, certain health conditions may also cause tinnitus.
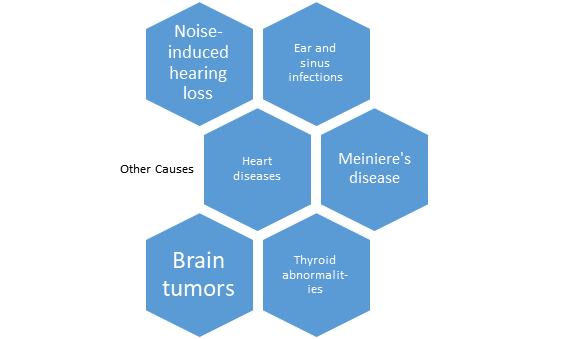
Risk Factors:
Cumulative and loud noise exposure, age, hearing loss, use of tobacco and alcohol, certain health conditions like heart problems, arthritis, etc. might elevates the risk of tinnitus.
Young-age vs. Old-age Onset Tinnitus:
The incidence of tinnitus increases with the increase in age and the most common onset is 60–69 years. Old people are prone to develop hearing loss, one of the biggest risk factors for tinnitus. However, young people, especially children, may also suffer from this condition. Children unlike adults are not able to distinguish between normal sounds and other sounds. The causes of tinnitus in children/adults are usually the same as in old-age people.
Subjective vs. Objective Tinnitus:
| Subjective | Objective |
| Common | Less common |
| Caused by damage to outer/middle or inner ear | Caused by damage to middle ear bone/ blood vessel issues/muscle contractions |
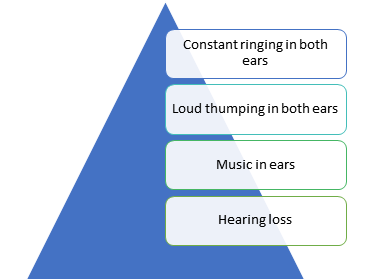
Early Signs for Recognizing Tinnitus
Treatment for Tinnitus
The treatment is usually based on the underlying cause of tinnitus.
- Removal of earwax: helps in decreasing the symptoms of tinnitus
- Hearing aids: Tinnitus caused by age-related or noise-related hearing loss can be improved by hearing aids
- Health condition or blood vessel problem: Medications or surgery for treating an underlying health condition or blood vessel problem may reduce the symptoms associated with tinnitus
Other treatment/management options:
- Noise suppression: The ringing or other noises can be suppressed by using certain electronic devices such as
White noise machines: The use of electronic devices such as fans, ACs, humidifiers, etc. is one of the effective treatments for tinnitus as they produce sounds similar to environmental sounds. These devices help make tinnitus less perceptible at night and promotes healthy sleep.
Mashing devices: These devices are similar to hearing aids and produce low-level but continuous white noise in patients with tinnitus. - Counseling: Certain therapies could help people to live and manage tinnitus:
Retraining therapy: This therapy includes a combination of sound masking and counseling by an audiologist or trained professional. The therapy is useful for masking the symptoms of tinnitus.
Cognitive behavioral therapy: An individualized program by a psychologist or trained medical professional can help to cope up with the stress or depression due to tinnitus. - Medications: Medications can help to manage the symptoms and reduce the severity of complications associated with tinnitus. Tricyclic antidepressants such as amitriptyline and nortriptyline are the two most commonly prescribed medications used to manage mental health.