Definition
Surgery for tumors of the parotid and submandibular glands involves the removal of abnormal growths or tumors located within these salivary glands. These tumors can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous), and surgical intervention is often necessary for diagnosis and treatment.
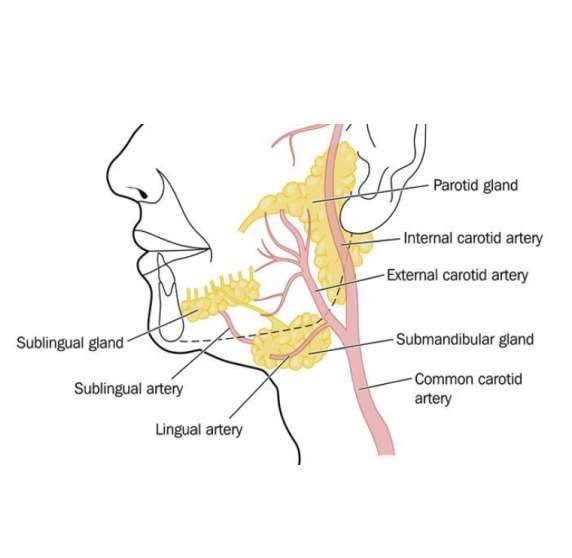
Causes of Tumors of Parotid and Submandibular Glands
Tumors in these glands can arise due to various factors, including:
Benign Parotid Tumors: The most common cause is benign growths like pleomorphic adenoma.
Malignant Tumors: Cancerous tumors, such as mucoepidermoid carcinoma or adenoid cystic carcinoma, can develop.
Salivary Gland Stones: Obstruction or inflammation of the salivary ducts can lead to the formation of tumors.
Radiation Exposure: Previous radiation therapy in the head and neck region may increase the risk.
Family History: A family history of salivary gland tumors can be a predisposing factor.
Symptoms of Tumors of Parotid and Submandibular Glands
The symptoms of submandibular gland tumor associated with these tumors can vary but may include:
Lump or Swelling: A painless or painful lump in the cheek, jaw, or neck.
Facial Weakness: If the facial nerve is affected, facial weakness or paralysis may occur.
Pain or Discomfort: Some tumors can cause pain, tenderness, or discomfort in the affected gland.
Changes in Saliva: Altered saliva production, taste changes, or dry mouth.
Difficulty Swallowing: If the tumor compresses the throat or food pipe, swallowing difficulties may arise.
Ear Pain: Pain in the ear on the same side as the affected gland.
Neck Swelling: Enlargement of lymph nodes in the neck if the tumor is cancerous.
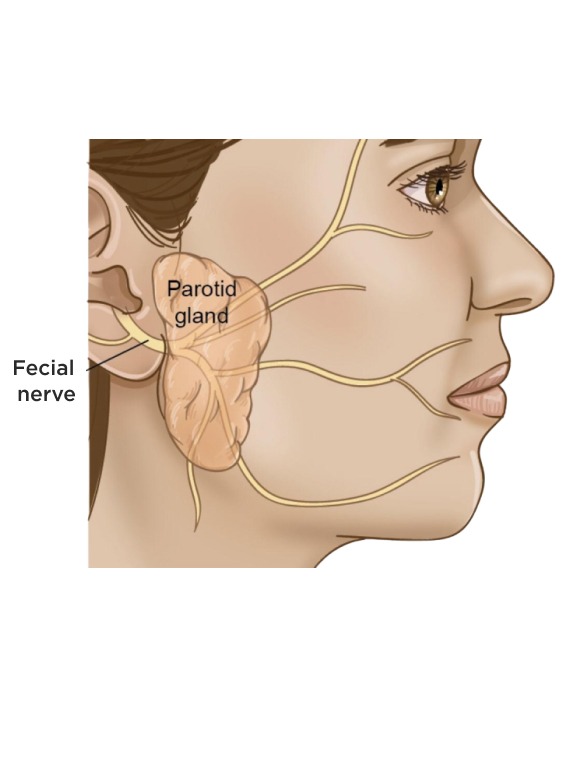
Treatment of Tumors of Parotid and Submandibular Glands
Treatment options depend on the nature of the tumor (benign or malignant), its size, location, and patient-specific factors:
Surgery: Surgical removal of the tumor, called a parotidectomy or submandibular gland excision, is often the primary treatment..
Biopsy: Tissue samples may be taken during surgery to determine if the tumor is cancerous.
Radiation Therapy: In cases of malignant tumors, radiation therapy may be recommended post-surgery.
Chemotherapy: In some advanced cases of malignant tumors, chemotherapy may be considered.
Facial Nerve Preservation: In surgeries for parotid tumors ,facial nerve monitoring may be used to avoid inadvertent injury to the facial nerve.
Hearing Loss: Temporary or fluctuating hearing loss in some cases.
Management and Postoperative Care:
Following surgery, patients may need to:
Manage Pain: Pain management medications may be prescribed.
Physical Therapy : Facial exercises and therapy can aid in recovery and preserve facial function.
Regular Follow-Ups: Scheduled follow-up appointments are essential to monitor recovery and manage any complications.
Lifestyle Adjustments: Adjustments to diet and self-care may
be necessary, especially if saliva production is affected.
Summary
Surgery for tumors of the parotid and submandibular glands involves the removal of abnormal growths, which can be benign or malignant. Symptoms may include lumps, facial weakness, pain, and difficulty swallowing. Treatment options include surgical removal, biopsy, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy, depending on the tumor’s nature and extent. Postoperative care, including pain management and rehabilitation, is crucial for a successful recovery.

