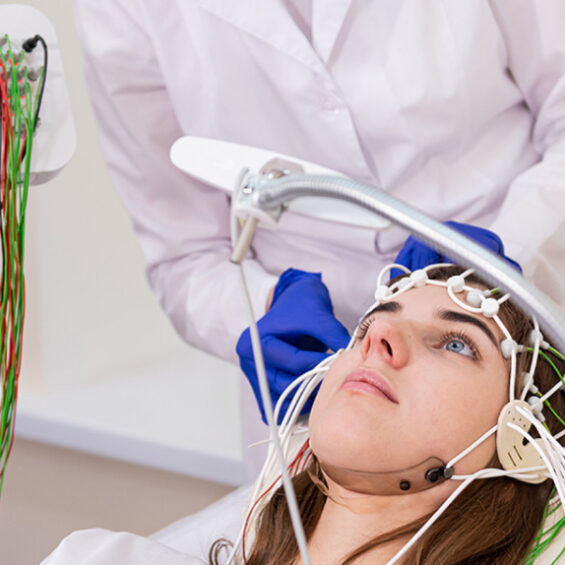
Definition
A sleep study, also known as polysomnography, is a medical examination that involves monitoring various physiological parameters during sleep. It is used to diagnose and assess sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea, insomnia, and restless leg syndrome.
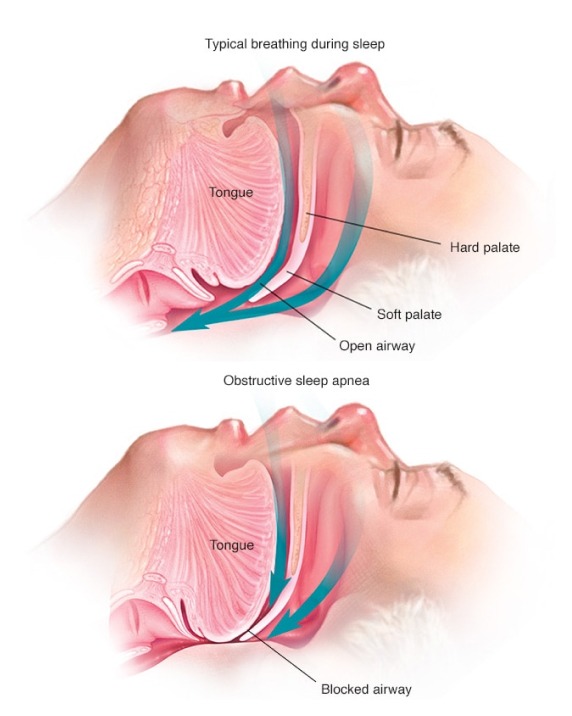
Causes of a Sleep Study
A sleep study is typically conducted when an individual experiences symptoms or risk factors associated with sleep disorders. Common reasons for a sleep study cause include:
Suspected Sleep Apnea: Symptoms like loud snoring, choking or gasping during sleep, and excessive daytime sleepiness may indicate sleep apnea.
Insomnia: Persistent difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep.
Narcolepsy: Sudden, uncontrollable episodes of falling asleep during the day.
Restless Leg Syndrome: Uncomfortable sensations in the legs that disrupt sleep.
Parasomnias: Sleepwalking, night terrors, or other abnormal behaviors during sleep.
Symptoms Requiring a Sleep Study
The sleep disorders symptoms or risk factors that may prompt a sleep study include:
Loud Snoring: Especially if it is accompanied by pauses in breathing.
Excessive Daytime Sleepiness: Feeling persistently tired despite spending adequate time in bed.
Difficulty Breathing During Sleep: Gasping for air or choking during the night.
Morning Headaches: Frequent headaches upon waking.
Leg Discomfort: Unexplained leg discomfort or the urge to move the legs at night.
Frequent Awakening: Waking up multiple times during the night and having trouble falling back asleep.
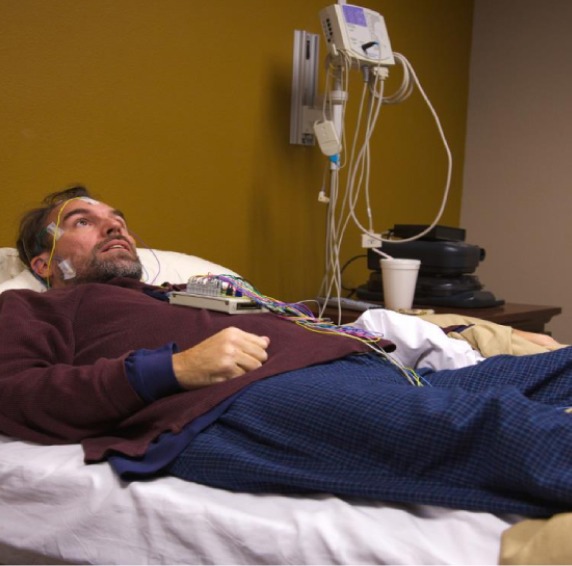
Treatment and Management
The treatment and management of sleep disorders identified through a sleep disorders treatment depend on the specific diagnosis. Common approaches include:
CPAP or BiPAP Therapy: Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) or bilevel positive airway pressure (BiPAP) devices are used to treat sleep apnea by maintaining open airways during sleep.
Medications: Medications may be prescribed to address conditions such as insomnia or restless leg syndrome.
Lifestyle Modifications: Implementing changes like weight loss, regular exercise, and sleep hygiene practices can improve sleep quality.
Behavioral Therapies: Cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia (CBT-I) can help individuals address insomnia through therapy-based techniques.
Surgical Interventions: In some cases, surgical procedures may be considered to treat sleep apnea or other structural issues affecting sleep.
Management and Prevention
To manage and prevent sleep disorders:
Sleep Hygiene: Practice good sleep habits, including maintaining a regular sleep schedule and creating a comfortable sleep environment.
Weight Management: Achieve and maintain a healthy weight, as excess weight can contribute to sleep apnea and other sleep disorders.
Avoid Stimulants: Limit or avoid caffeine and nicotine, especially in the evening.
Stress Management: Employ stress-reduction techniques to alleviate anxiety that can affect sleep
Regular Check-Ups: Routine check-ups and consultations with sleep specialists can help detect and address sleep disorders early.
Summary
A sleep study, or polysomnography, is a diagnostic tool used to evaluate and diagnose sleep disorders such as sleep apnea, insomnia, and restless leg syndrome. It is conducted when individuals experience symptoms like loud snoring, excessive daytime sleepiness, or difficulties breathing during sleep. Treatment and management options depend on the specific diagnosis and may include therapies, lifestyle modifications, and medications. Practicing good sleep hygiene and seeking timely medical evaluation are key to addressing and preventing sleep disorders.