What are Benign and Malignant Thyroid Tumors?
Benign and malignant thyroid tumors are two different types of growths or masses that can develop in the thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped organ located in the front of the neck, just below the Adam’s apple. The thyroid gland plays a crucial role in producing hormones that regulate various bodily functions, including metabolism.
Benign Thyroid Tumors (Thyroid Nodules)
Definition: Benign thyroid tumors are non-cancerous growths or nodules that develop within the thyroid gland.
Characteristics: Benign thyroid nodules are typically slow-growing and do not invade surrounding tissues. They are usually encapsulated, meaning they are contained within a fibrous capsule.
Common Types: Common types of benign thyroid nodules include colloid nodules, adenomas, and thyroid cysts.
Symptoms: Most benign thyroid nodules do not cause symptoms and are discovered incidentally during a physical examination or imaging tests. However, larger nodules can sometimes lead to symptoms such as difficulty swallowing, neck discomfort, or visible neck swelling (goiter).
Malignant Thyroid Tumors (Thyroid Cancer)
Definition: Malignant thyroid tumors are cancerous growths that originate in the cells of the thyroid gland. There are several types of thyroid cancer, with papillary and follicular carcinomas being the most common.
Characteristics: Thyroid cancer cells can invade nearby tissues and may spread (metastasize),although rarely, to other parts of the body, such as lymph nodes and distant organs, if not treated early.
Common Types: Common types of thyroid cancer include papillary carcinoma, follicular carcinoma, medullary carcinoma, and anaplastic carcinoma.
Symptoms: Thyroid cancer may present with symptoms such as a painless lump or nodule in the neck, hoarseness, difficulty swallowing, or swollen lymph nodes in the neck.
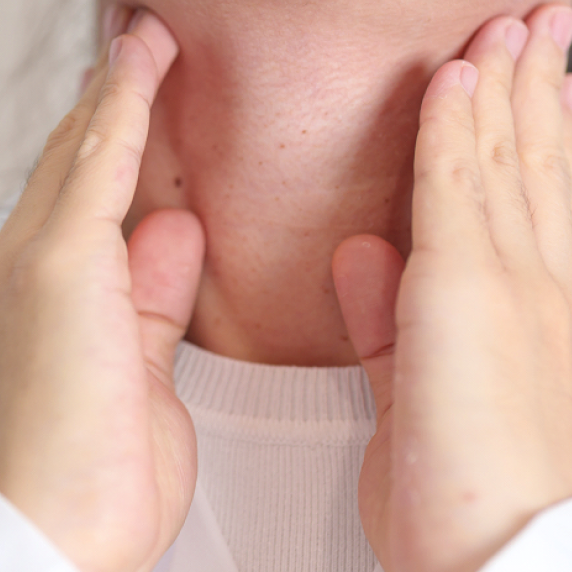
Investigations
- Thyroid hormone assay including tests for thyroid antibodies.
- Diagnostic laryngoscopy to rule out Vocal cord paresis/palsy.
- FNAC of the suspicious lesion
- Imaging studies including USG ,CECT,MRI and in some cases PET Scan.
- Nuclear scans in patients with hyperthyroidism to rule out “Hot and Cold”nodules.
Treatments
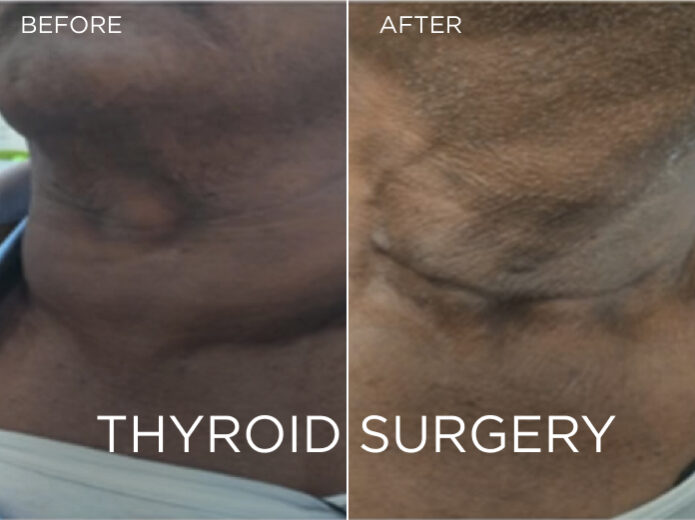
Surgery is a common treatment option for both benign (non-cancerous) and malignant (cancerous) thyroid tumors. The type of surgery performed depends on several factors, including the type of tumor, its size, location, and the patient’s overall health.
Here’s an overview of surgical options for benign and malignant thyroid tumors:
Benign Thyroid Tumors
Thyroid Lobectomy: This surgery involves the removal of one lobe (half) of the thyroid gland. It is often performed when the benign tumor is confined to one lobe, and the remaining healthy thyroid tissue can continue to function adequately.
Total Thyroidectomy: In cases where the benign tumor is large, causing symptoms, or when there are multiple tumors in both lobes, a complete thyroidectomy may be recommended. This procedure involves the removal of the entire thyroid gland.
Malignant Thyroid Tumors (Thyroid Cancer)
Total Thyroidectomy: Total thyroidectomy is the most common surgical treatment for thyroid cancer. It involves the complete removal of the thyroid gland, as well as any nearby lymph nodes that may be affected.
Lymph Node Dissection: In some cases of thyroid cancer, especially if the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes, a lymph node dissection may be performed to remove affected lymph nodes. This can help prevent the cancer from spreading further.
Radioactive Iodine (RAI) Treatment: After surgery for certain types of thyroid cancer, such as papillary or follicular carcinoma, radioactive iodine therapy may be administered to destroy any remaining thyroid tissue or cancer cells.
In addition to these surgical procedures, there are minimally invasive techniques, such as endoscopic thyroidectomy, which may be considered in some cases. The choice of surgery and the extent of the procedure depend on factors like the type and stage of cancer, the patient’s age, overall health, and personal preferences.
At Dr. Ram ENT Hospital, we understand the importance of comprehensive care and specialized treatment for thyroid tumors. Thyroid tumors can be either benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous), and each requires a tailored approach to ensure the best possible outcomes. Our team of skilled surgeons and healthcare professionals provides top-notch surgical interventions for patients with thyroid tumors.
Patient-Centered Care
At Dr. Ram ENT Hospital, our patient-centered approach ensures that you receive personalized care throughout your treatment journey. We prioritize your comfort, safety, and well-being at every step of the process.
Recovery and Follow-up
Following surgery, our dedicated team provides comprehensive postoperative care and guidance. Regular follow-up appointments are scheduled to monitor your progress and adjust treatment as necessary.
Before And After Gallery