Definition
Tonsillitis and adenoiditis are inflammatory conditions affecting the tonsils and adenoids, respectively. These are collections of lymphoid tissue located in the throat and nasal passages, and they play a role in the immune system. When infected, they can lead to various symptoms and discomfort.
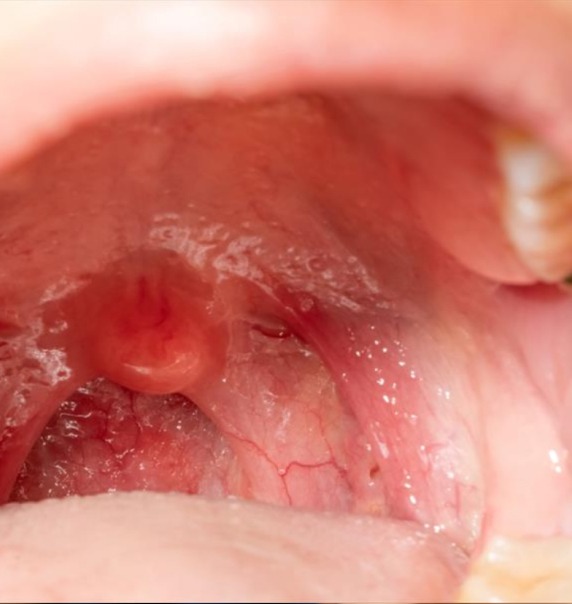
Causes of Tonsillitis and Adenoiditis
These conditions can be caused by:
Viral Infections: Viruses, such as the common cold or Epstein-Barr virus, can lead to inflammation of the tonsils and adenoids.
Bacterial Infections: Streptococcus bacteria (strep throat) are a common cause of tonsillitis. Adenoiditis may result from bacterial overgrowth.
Recurrent Infections: Frequent infections can lead to chronic inflammation of the tonsils and adenoids.
Allergies: Allergic reactions can cause inflammation and enlargement of these tissues.
Environmental Factors: Exposure to irritants or pollutants can contribute to inflammation.
Symptoms of Nose Bleeds
Tonsillitis :
Sore Throat: Pain and discomfort in the throat.
Difficulty Swallowing: Painful or difficult swallowing.
Fever: Elevated body temperature, especially in bacterial cases.
Swollen Tonsils: Enlarged, red, and swollen tonsils
White or Yellow Patches: Pus-filled patches on the tonsils.
Bad Breath: Foul-smelling breath due to infection.
Adenoiditis:
Nasal Congestion: Difficulty breathing through the nose.
Snoring: Noisy breathing during sleep
Breathing Problems: Particularly in children, it can lead to breathing through the mouth.
Sore Throat: Due to postnasal drip.
Adenoid facies: Prolonged mouth breathing causes malformation of the face with protruding chin, high arched palate, dental misalignment and retracted cheek bones.
Treatment of Tonsillitis and Adenoiditis
Treatment of Tonsillitis depends on the underlying cause and severity:
Antibiotics: Bacterial infections are treated with antibiotics
Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers can alleviate discomfort.
Rest and Hydration: Resting and staying hydrated help the body recover.
Surgery: In cases of recurrent or severe infections, surgical removal of the tonsils (tonsillectomy) or adenoids (adenoidectomy) may be recommended.
Management and Prevention
To manage and prevent these conditions:
Hand Hygiene: Frequent hand washing helps prevent the spread of infections
Avoid Irritants: Reduce exposure to allergens or irritants.
Stay Hydrated: Adequate hydration supports immune function.
Corticosteroid nasal sprays: Allergy management plays a major role, especially in adenoiditis.
Vaccination: Some vaccines can prevent infections that cause tonsillitis and adenoiditis.
Summary
Tonsillitis and adenoiditis are inflammatory conditions of the tonsils and adenoids, respectively, often caused by infections, allergies, or environmental factors. Symptoms include sore throat, difficulty swallowing, fever, nasal congestion, and snoring. Treatment options include antibiotics, pain relievers, rest, and in some cases, surgical removal. Prevention involves hand hygiene, avoiding irritants, and vaccination. If you or your child experiences recurrent or severe symptoms, consult a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.

