Definition
Cholesteatoma is a medical condition characterized by the abnormal growth of skin cells within the middle ear, typically behind the eardrum. This growth can lead to various complications and hearing problems and requires prompt attention.
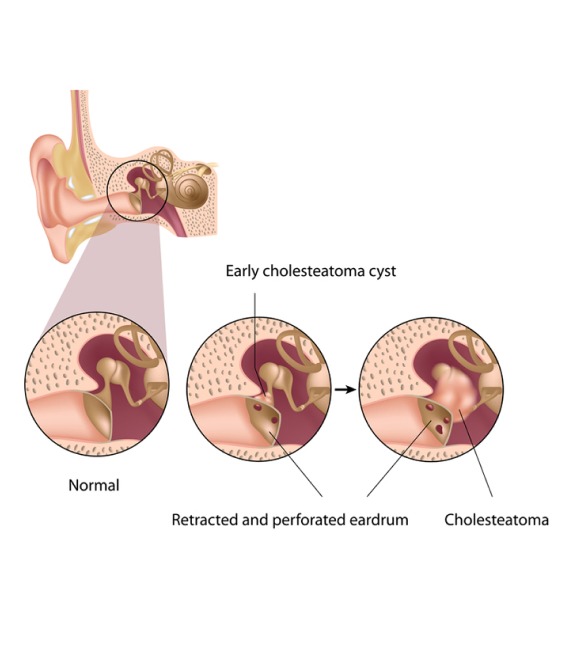
Causes of Cholesteatoma
Tinnitus can have various underlying causes, including:
Congenital: Some cases of cholesteatoma are present at birth, while others develop later in life due to other factors.
Chronic Ear Infections: Repeated or untreated ear infections can increase the risk of cholesteatoma formation.
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction: Problems with the Eustachian tube can create a vacuum effect, pulling skin into the middle ear
Trauma: Injury to the ear can sometimes trigger the growth of cholesteatoma tissue.
Previous Ear Surgeries: Surgical procedures involving the ear can inadvertently lead to cholesteatoma formation in rare cases.
Symptoms of Cholesteatoma
The symptoms of cholesteatoma may include:
Ear Discharge: Foul-smelling discharge from the ear is a common sign.
Hearing Loss: Gradual hearing loss, which may worsen over time.
Ear Pain: Chronic ear pain or discomfort, often associated with ear infections.
Tinnitus: Ringing or buzzing in the affected ear.
Vertigo: Dizziness or balance problems, especially if the inner ear is affected.
Fullness Sensation: A feeling of fullness or pressure in the affected ear.
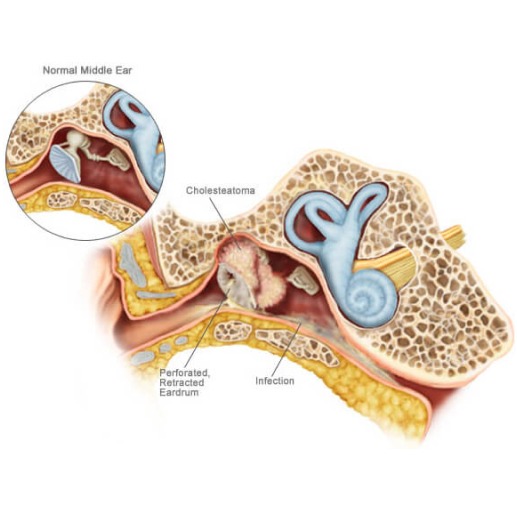
Treatment of Cholesteatoma
Cholesteatoma treatment typically involves surgical intervention to remove the abnormal tissue and prevent complications. The specific approach may vary based on the extent of the cholesteatoma and individual patient factors:
Surgery: A surgical procedure, such as a tympanoplasty or mastoidectomy, is often required to remove the cholesteatoma and reconstruct any damaged structures within the ear.
Antibiotics: Antibiotics may be prescribed before or after surgery to manage or prevent infection.
Hearing Restoration: In cases of significant hearing loss, additional procedures like ossicular chain reconstruction may be performed to restore hearing.
Follow-Up Care: Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor the ear’s healing and address any complications promptly.
Management and Prevention:
After successful treatment, ongoing monitoring and care are essential to prevent cholesteatoma recurrence and manage any residual hearing issues. Preventive measures include:
Prompt Treatment of Ear Infections: Treating ear infections promptly can reduce the risk of cholesteatoma formation.
Ear Protection: Using ear protection in noisy environments or during water activities can prevent trauma and damage to the ear.
Regular Check-Ups: Routine ear examinations by an ear, nose, and throat specialist can help detect cholesteatoma in its early stages.
Summary
In summary, cholesteatoma is a condition characterized by the growth of abnormal skin cells within the middle ear, leading to various ear-related symptoms and complications. Prompt diagnosis and surgical intervention are typically required for effective treatment. After treatment, ongoing care and preventive measures are essential to ensure the best possible outcome and minimize the risk of recurrence. If you experience symptoms suggestive of cholesteatoma, seek immediate evaluation and guidance from a healthcare professional preferably an ear, nose, and throat specialist.


