Definition
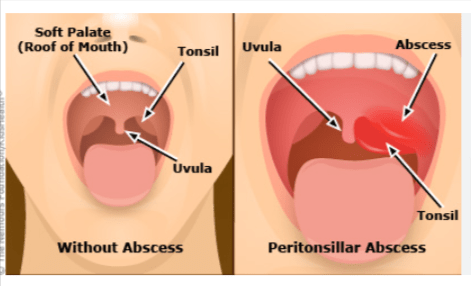
A Peritonsillar abscess, also known as a quinsy, is a painful collection of pus that forms in the tissues surrounding one of the tonsils. This condition can cause severe throat pain and difficulty swallowing.
Causes of Peritonsillar Abscess
Peritonsillar abscesses typically develop as a complication of untreated or inadequately treated tonsillitis. The infection can spread to the surrounding tissue, leading to the formation of an abscess. peritonsillar abscess causes include:
Bacterial Infection: Usually, Streptococcus bacteria are the culprits behind peritonsillar abscesses.
Recurrent Tonsillitis: Individuals with frequent or chronic tonsillitis are at a higher risk.
Weakened Immune System: Immune system deficiencies can make one more susceptible.
Age: Young adults and adolescents are more commonly affected.
Symptoms of Peritonsillar Abscess
Peritonsillar abscesses are associated with several distressing symptoms, including:
Severe Throat Pain: Intense, often unilateral, pain on one side of the throat.
Difficulty Swallowing: Pain and discomfort while swallowing, which can lead to dehydration and weight loss.
Muffled Voice: Speech may sound muffled or unusual due to swelling.
Fever: Elevated body temperature is common with infections.
Swollen Tonsil: The affected tonsil is visibly swollen and may push the uvula to the opposite side.
Bad Breath: Foul-smelling breath may result from the infection.
Treatment of Peritonsillar Abscess
Prompt treatment is crucial for peritonsillar abscesses to prevent complications. peritonsillar abscesses Treatment options include:
Drainage: The abscess is drained by an ear, nose, and throat specialist using a needle or a small incision.
Antibiotics: Antibiotics are prescribed to treat the underlying infection.
Pain Relief: Over-the-counter or prescription pain relievers help manage severe throat pain.
Fluid and Nutrition: Intravenous (IV) fluids may be needed to maintain hydration and nutrition.
Tonsillectomy: In some cases, the tonsils may need to be removed to prevent recurrent abscesses.
Management and Prevention
To manage and prevent peritonsillar abscesses:
Prompt Tonsillitis Treatment: Treat tonsillitis promptly to prevent it from progressing to an abscess.
Good Oral Hygiene: Maintain good oral hygiene practices.
Stay Hydrated: Adequate fluid intake is crucial to prevent dehydration.
Avoid Smoking and Alcohol: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can increase the risk.
Regular Medical Check-Ups: Seek medical attention for recurring tonsillitis or severe throat pain.
Summary
A peritonsillar abscess is a painful condition characterized by the formation of pus around one of the tonsils, usually as a complication of untreated tonsillitis. Symptoms include severe throat pain, difficulty swallowing, and fever. Treatment involves drainage, antibiotics, and pain relief, with surgical removal of the tonsils sometimes necessary. Prevention includes timely treatment of tonsillitis and maintaining good oral hygiene.


