Definition
Hearing loss refers to a partial or complete inability to hear sounds in one or both ears. It can vary in severity from mild to profound and can affect people of all ages.
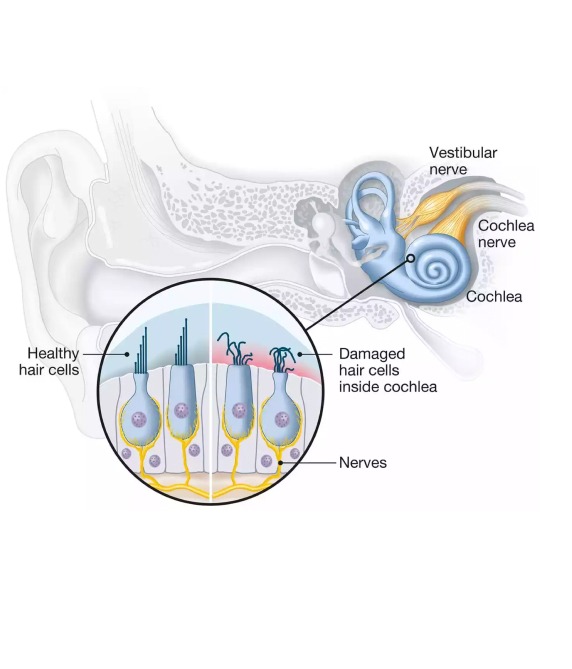
Causes of Hearing Loss
Age-related (Presbycusis): Gradual hearing loss as a natural part of aging.
Noise-induced: Prolonged exposure to loud noises, such as in workplaces or through recreational activities like concerts and shooting.
Genetic factors: Some people may have a genetic predisposition to hearing loss.
Infections: Ear infections, particularly in childhood, can damage the ear and lead to hearing loss.
Medications: Certain medications, known as ototoxic drugs, can harm the ear and cause hearing loss.
Trauma: Head injuries or a punctured eardrum can result in hearing loss.
Medical conditions: Conditions like Meniere’s disease, otosclerosis, and autoimmune disorders can impact hearing.
Excessive earwax: A buildup of earwax can block the ear canal and cause temporary hearing loss.
Symptoms of Hearing Loss
The symptoms of hearing loss can vary depending on its type and severity. Common symptom include:
1. Difficulty in understanding speech, especially in noisy environments.
2. Frequently asking others to repeat themselves.
3. Turning up the volume on electronic devices.
4. Avoiding social situations or withdrawing from conversations.
5. Ringing or buzzing in the ears (tinnitus).
6. Ear pain or discomfort (in the case of infections or trauma).

Treatment of Hearing Loss
The treatment for hearing loss depends on its cause and severity:
Hearing Aids: These devices amplify sound and are effective for many people with hearing loss, especially in cases of age-related or mild to moderate hearing loss.
Cochlear Implants: For severe to profound hearing loss especially in very young children and infants, cochlear implants can be surgically implanted to stimulate the auditory nerve directly.
Medication: If hearing loss is due to an underlying medical condition or infection, medications may be prescribed to address the root cause.
Surgery: If hearing loss is due to an perforated ear drum, damaged ossicles or fixed ossicles(Otosclerosis) surgery (tympanoplasty/ossiculoplasty/stapedotomy) can help improve hearing).
Earwax Removal: If hearing loss is due to earwax buildup, an ENT specialist can safely remove the blockage.
Lifestyle Changes: Protecting your ears from loud noises, using earplugs, and managing underlying health conditions can help prevent or manage hearing loss.
Communication Strategies: Learning sign language or lip-reading and improving communication skills can be valuable for those with hearing loss.
Summary
Hearing loss is the reduced ability to hear sounds, which can result from various causes such as aging, noise exposure, genetics, infections, medications, trauma, or medical conditions. Symptoms include difficulty understanding speech, ringing in the ears, and increased volume settings on devices. Treatment options range from hearing aids and cochlear implants to medication, surgery and lifestyle changes. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for managing hearing loss and improving quality of life. It’s essential to consult with an ENT specialist for proper evaluation and guidance on the most suitable treatment approach.

