The ear is one of the most common areas of your body that can become infected, especially in young children. While most infections are mild and resolve with simple home care, there are times when an abscess or mastoiditis will develop. This is where you need to see your doctor about treatment for your ear infection.
If you notice any of these symptoms for more than two days, see your doctor without delay: pain during swallowing or hearing loss. This means that the infection has reached an advanced stage and requires urgent treatment.
What is an Ear Infection?
Ear infections (also called otitis media) are one of the most common reasons why babies and toddlers visit the doctor and miss school and other activities. Most often, an ear infection follows a cold or other respiratory illness and can be easily treated with antibiotics. However, if your child has more than three ear infections in one year, he or she may have what’s called recurrent ear infections.
Symptoms of Ear Infection
In adults, the symptoms are simple. Adults with ear infections experience ear pain and pressure, fluid in the ear, and reduced hearing. Children experience a wider range of signs. These include:
- tugging or pulling at the ear
- ear pain, especially when lying down
- difficulty sleeping
- crying more than normal
- loss of balance
- difficulty hearing
- fever
- lack of appetite
- headache
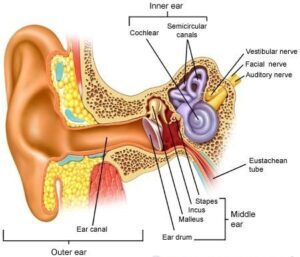
Types of Ear Infection
Generally, ear infections are divided into three categories: external otitis, middle ear infection and inner ear infection.
Acute otitis media (AOM)
AOM is the most common type of bacterial ear infection. Acute otitis media (AOM) often strikes without warning and may cause fever, nausea, difficulty to swallow, or vomiting. It can also make your child feel extremely uncomfortable; he or she might pull at the ears because of ear pain, complain of itching or irritation inside the ear canal, or complain of hearing loss.
Otitis media with effusion (OME)
Otitis media with effusion, also known as OME, is often due to an ear infection. When the infection has run its course, there may be some fluid left behind the eardrum. A person with OME may not experience any symptoms, but a doctor will be able to spot the remaining fluid.
Chronic otitis media with effusion (COME)
Otitis media with effusion (OME) is a common cause of middle ear disease in children. Treatment generally starts with watchful waiting for resolution of the effusion. If the fluid persists, or if there are signs of infection, then can consider decongestant therapy if only one side is involved, or antibiotic therapy if both sides are involved.